Agile Methodology
Agile Methodology
- Vocab for Agile Methodology and CSP
- What Is Agile Methodology in Project Management?
- Agile methodologies overview
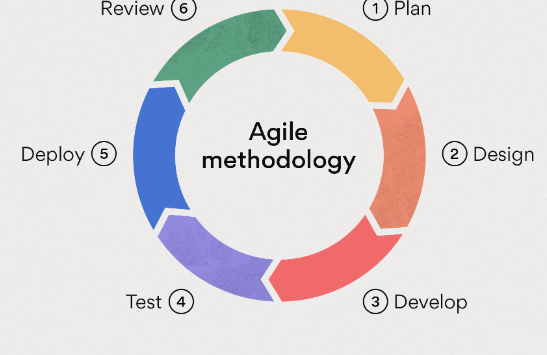
Vocab for Agile Methodology and CSP
-
scrum master- manage scrum board and ensure agile framework is followed, track issues and looks for opportunities for team to improve
-
DevOps- combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools that increase a team’s ability to deliver applications and services at high velocity
-
Frontend Developer- develops what users interact with
-
Backend Developer- develops what goes on behind the scenes, what the user doesn’t see, technical stuff
What Is Agile Methodology in Project Management?
The Agile methodology is a way to manage a project by breaking it up into several phases. It involves constant collaboration with stakeholders and continuous improvement at every stage. Once the work begins, teams cycle through a process of planning, executing, and evaluating. Continuous collaboration is vital, both with team members and project stakeholders.
Agile methodologies overview
-
The Agile Manifesto of Software Development put forth a groundbreaking mindset on delivering value and collaborating with customers when it was created in 2001. Agile’s four main values are:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
Skills
- Creativity
- Conceptualize problems and solutions
- Display foresight
- Make connections
- Make intelligent inferences
- Synthesize ideas and data
- Critical Thinking
- ability to take a step back and look at things more critically
- ‘Where might we have to have gotten this wrong?’
- ‘How might we be able to improve this?’ is critical thinking?
- Critical thinkers head off problems before they arise
- ability to take a step back and look at things more critically
- Communication
- Effective communication is the crux of everything you do. It doesn’t matter how creative or intelligent you are, or how many computer languages you know: If you can’t communicate well, your other skills are meaningless. Students are encouraged to talk about how they were able to bring their teams together.
- Verbal skills. How do you address an audience in terms they can understand.
- Listening skills. Learning and understanding without defensiveness.
- Writing skills. You need to be able to write in such a way that non-experts will understand.
- Technological communication skills. You should be able to discuss highly technical hard skills in a way appropriate to your audience. Communication details are not the same for all audiences.
- Effective communication is the crux of everything you do. It doesn’t matter how creative or intelligent you are, or how many computer languages you know: If you can’t communicate well, your other skills are meaningless. Students are encouraged to talk about how they were able to bring their teams together.
- Collaboration through Leadership
- Leadership skills generally encompass communication, problem-solving and managing conflict, relationship building and being able to get people on your team on board with a mission or project. Leaders are big-picture thinkers who take various interests into account when making major decisions. Leaders are responsible for:
- Delegating responsibility
- Demonstrating effective time management
- Initiating new ideas
- Major decision-making
- Managing conflict
- Managing groups
- Multitasking
- Teaching and mentoring
- Leadership skills generally encompass communication, problem-solving and managing conflict, relationship building and being able to get people on your team on board with a mission or project. Leaders are big-picture thinkers who take various interests into account when making major decisions. Leaders are responsible for:
- Collaboration
- Teamwork Individuals that work well with others. This is a important category mentioned in early school. But it applies to High School, College and adults. Trust is the major difference between working alone versus working in groups. And trust can be hard: Some people are skeptical by nature or want to work through an entire project lifecycle solo. But placing trust in an active, dynamic team provides more than just project completion. Teamwork — a sense of community — elevates spirits and improves productivity.
- Accepting responsibility
- Making and implementing decisions
- Managing time wisely
- Meeting both short- and long-term goals
- Organizing
- Setting and meeting deadlines
- Researching
- Research is not a process performed by Teacher, Boss, or some upstream process. Everything you do in Technology requires research. Research is a key part of the lifecycle: changing plans, fluctuating results, and roadblocks require research before anyone can take action. Conversing with team members is a form of research: If you’ve asked a peer’s opinion on a technical matter, you’ve performed research.
- Analyzing information
- Brainstorming solutions
- Delineating needs and requirements
- Extracting information from data
- Gathering information
- Forecasting possible roadblocks
- Setting goals
- Solving problems
- Research is not a process performed by Teacher, Boss, or some upstream process. Everything you do in Technology requires research. Research is a key part of the lifecycle: changing plans, fluctuating results, and roadblocks require research before anyone can take action. Conversing with team members is a form of research: If you’ve asked a peer’s opinion on a technical matter, you’ve performed research.
- Technical
- We live in a tech-heavy world, and you need to understand the tech your project requires. Try to stay current with the many technical advancements on your project. Make sure that play with the different softwares and platforms that are part of your environment. Be knowledgeable and speak to the technical things that you are learning.
- Being easy to work with
- Quick to learn
- Glad to learn
- Failing and always willing to try new things
- Willing to open new doors in case of a drastic oversight
- We live in a tech-heavy world, and you need to understand the tech your project requires. Try to stay current with the many technical advancements on your project. Make sure that play with the different softwares and platforms that are part of your environment. Be knowledgeable and speak to the technical things that you are learning.